BEIJING, June 17 (Reuters) – China’s May industrial output lagged expectations and a slowdown in the property sector showed no signs of easing despite policy support, adding pressure on Beijing to shore up growth.
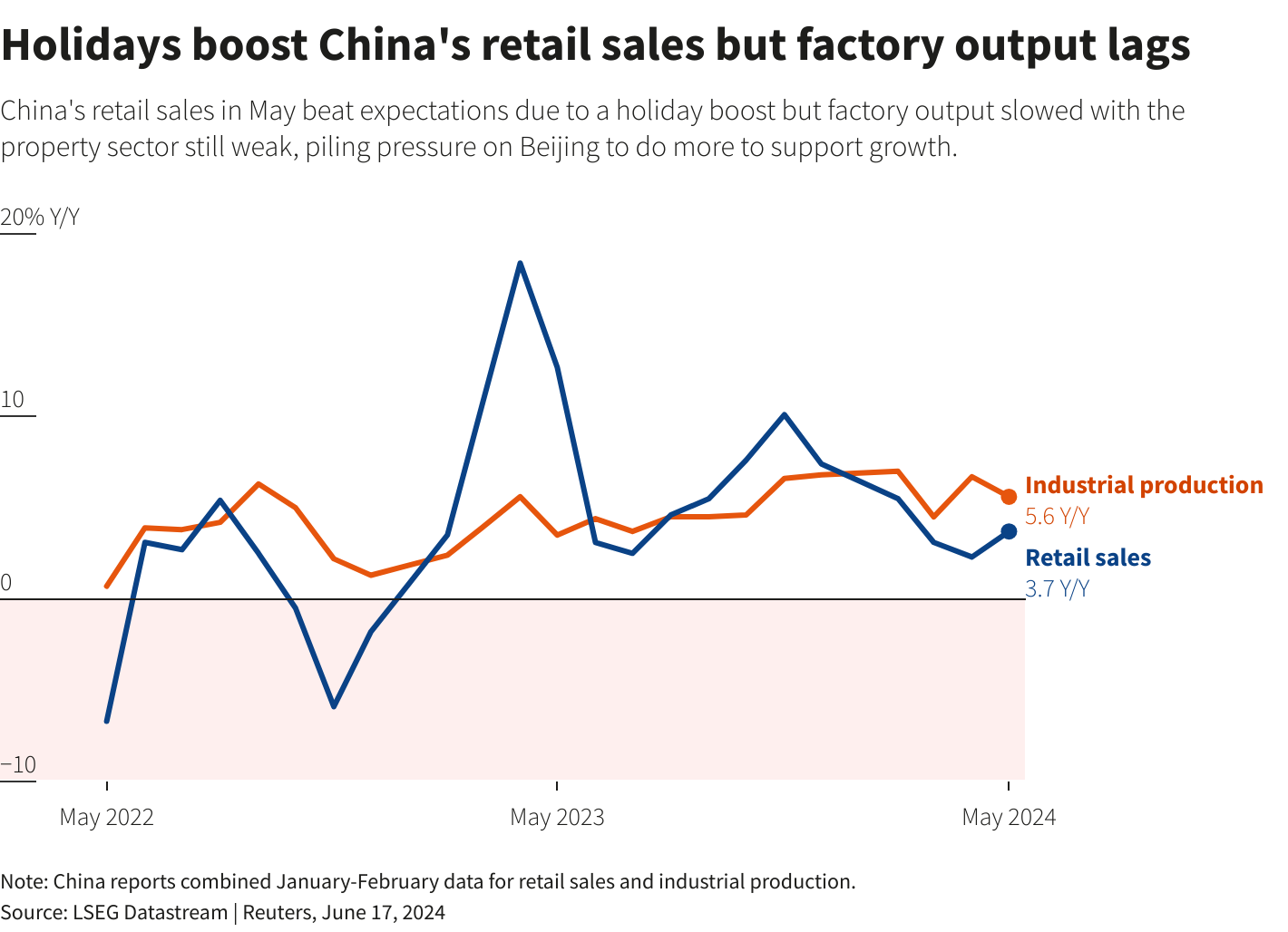
Apart from retail sales that beat forecasts due to a holiday boost, the flurry of data on Monday was largely downbeat, underscoring a bumpy recovery for the world’s second-largest economy.
May industrial output grew 5.6% from a year earlier, National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) data showed, slowing from the 6.7% pace in April and below expectations for a 6.0% increase in a Reuters poll of analysts.
However, retail sales, a gauge of consumption, in May rose 3.7% on year, accelerating from a 2.3% rise in April and marking the quickest growth since February. Analysts had expected a 3.0% expansion due to a five-day public holiday earlier in the month.
“May activity data and our high-frequency trackers for the first half of June suggest significant cross-sector divergences remain in the economy – strong exports and manufacturing activity, relatively stable consumption, and still-depressed property activity,” Goldman Sachs analysts said in a note.
Fixed asset investment rose 4.0% in the first five months of 2024 from the same period a year earlier, versus expectations for a 4.2% rise. It grew 4.2% in the January to April period.
Manufacturing investment in the first five months showed robust growth of 9.6%, underpinned by China’s emphasis for “quality growth” through technological breakthroughs and innovation this year.
Private sector investment grew 0.1% in January-May, down from 0.3% in the first four months, pointing to still weak confidence among private businesses. By comparison, investment in the state sector jumped 7.1% in the first five months.
EXPORTS-LED RECOVERY
Exports helped bolster the economy, with steel and aluminium output posting sharp jumps in May.
“Exports drove industrial growth and manufacturing investment significantly, but real estate weakness still hit household consumption and investment,” said ZhaoPeng Xing, senior China strategist at ANZ.

China’s property market slump, high local government debt and deflationary pressure remain heavy drags on economic activity. The latest figures point to an uneven growth that reinforces calls for more fiscal and monetary policy support.
“We still see the likelihood of a cut to the Loan Prime Rate (LPR) this month, particularly on the 5-year tenor, as this will help banks to retain households’ mortgage loans,” said Zhou Hao, chief economist at Guotai Junan International.
But chief China economist at Citi Yu Xiangrong expects a total 20-basis-point policy rate reduction in the second half of this year, but no LPR cut on June 20.
PROPERTY DATA WORSEN
China’s economy grew a faster-than-expected 5.3% in the first quarter, but analysts say the government’s annual growth target of around 5% is ambitious as the property sector remains in the doldrums.
New home prices slipped 0.7% in May from April, marking the 11th straight month-on-month decline and steepest drop since October 2014, according to Reuters calculations based on NBS data.
NBS spokesperson Liu Aihua told a media briefing on Monday that the property market is undergoing adjustment and it will take some time for policy measures to kick in.
The property sector, which accounted for around a quarter of economic output before the downturn, has been hit by a regulatory crackdown as well as demographic and broad economic pressures. The government has launched a slew of measures to help homebuyers, such as easing mortgage rules.
The job market overall was steady. The nationwide survey-based jobless rate hit 5.0% in May, the same as that in April.
Beijing has vowed to create more jobs linked to major projects, promote domestic demand and pledged greater fiscal stimulus to shore up growth.
Sign up here.
Reporting by Albee Zhang, Ellen Zhang and Kevin Yao; Editing by Jacqueline Wong
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles.

